"Essential Elements of UI/UX Design: A Comprehensive Guide"
Essential Elements of UI/UX Design: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
- The goal of UI/UX design is to make digital products' user experiences simple and engaging.
- It includes User Experience (UX) design, which looks after usability and general user happiness, and User Interface (UI) design, which deals with the visual components and layout.
- UI/UX design plays a critical role in current digital products to draw in and keep people in a market that is becoming more and more competitive.
- Effective UI/UX design promotes brand loyalty, boosts conversion rates, and improves user engagement.
- In order to create user-friendly and aesthetically pleasing interfaces, it is necessary to comprehend user demands, preferences, and behaviours.
- UI/UX design shapes a brand's identity and reputation in the digital sphere by influencing consumers' perceptions of a company and its offerings.
- Users want seamless and engaging experiences across all devices and channels, therefore UI/UX design has become even more important as mobile devices and digital platforms proliferate.
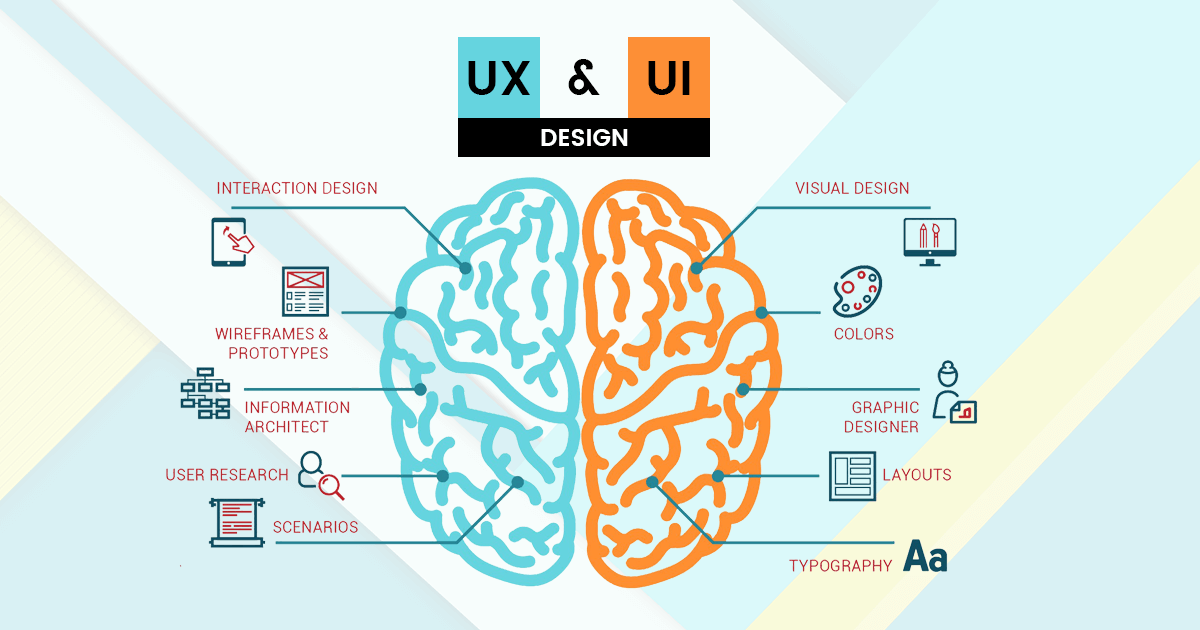
Elements of UX Design

User Research:
- Entails using techniques like surveys, interviews, and observation to get information about user needs, preferences, and behaviours.
- Aids in the understanding of the target market and their issues, directing the design process to produce solutions that deal with actual user issues.
Information Architecture:
- Focuses on setting up a digital product's information in a way that makes it easier to navigate and find.
- Consists of creating sitemaps, menus, and classification schemes to make sure users can find information and do activities with ease.
Wireframing:
- Include drawing digital or low-fidelity sketches of the functionality and design of the user interface.
- Helps to visualise the interface's flow and structure without concentrating on the specifics of the visual design, facilitating rapid iteration and feedback.
Prototyping:
- Entails creating high-fidelity, interactive user interface models in order to replicate the appearance and functionality of the finished product.
- Reduces the possibility of expensive errors by enabling designers to evaluate usability, functionality, and user interactions prior to investing in complete development.
Testing:
- Involves using user testing sessions to assess the UI/UX design's usability and efficacy.
- Identifies usability problems, collects input, and validates design choices by watching actual users engage with the product.
- Can employ methods to precisely evaluate user behaviour and preferences, such as eye-tracking studies, A/B testing, and usability testing.
Iterative Process:
- User research and testing results provide valuable insights that inform design iterations at every stage of the user experience design process.
- Iteration and continuous testing guarantee that the finished product satisfies user needs and provides a smooth and enjoyable user experience.
Translating Brand Identity:
- When it comes to converting brand identity components like the logo, colour scheme, and typography into digital interfaces, user interface design is essential.
- By maintaining consistency across a brand's offline and online presence, it strengthens awareness and recall of the brand at many touchpoints.
Colors:
- In user interface design, colour selection is crucial for expressing a brand's personality and generating particular feelings.
- Utilising brand colours consistently promotes brand association in consumers' minds and aids in creating visual continuity.
- A well-planned use of colour may direct users' gaze, draw attention to key components, and establish a unified visual hierarchy throughout the interface.
Typography:
- The choice of typography conveys the voice and tone of the brand and influences consumer perception of it as a whole.
- Maintaining a consistent font style throughout digital interfaces improves accessibility and readability while strengthening brand identity.
- Personalised typography or eye-catching type treatments can help set the company out even further and produce a visually striking identity.
Imagery:
- The aesthetic and values of the brand should be reflected in the images and visuals used in UI design.
- Brand identity is strengthened and desirable emotions are evoked when imaging styles, such as photography or illustration, are used consistently.
- Users are more receptive to authentic and pertinent images, which strengthens their bond with the business and enhances the user experience overall.
Branding Elements:
- In order to create a brand presence within the digital interface, UI design integrates branding components like logos, icons, and brand marks.
- Strategic placement of branding components strengthens brand association and increases credibility and trust in the brand.
- Users' brand loyalty is increased and brand recognition is improved by the interface's cohesive integration of branding elements.
Comments
Post a Comment