"8 Essential Principles for Effective Web Design"
8 Essential Principles for Effective
Web Design

Introduction
The act of organising, formulating, and carrying out a strategy to create a website that is both user-friendly and functional is known as web designing.
The importance of web design in creating engaging and successful websites:
- A user's first impression of a website is frequently shaped by its design, which also affects their decision to stay or go.
- A smooth and intuitive user experience is ensured by effective web design, which makes it simple for users to navigate, locate information, and carry out required tasks.
- A brand's identity, personality, and values are communicated through visual components like colours, font, and photography, and web design is essential to this process.
- Users are given confidence by a well-designed website, which communicates professionalism, dependability, and credibility—all of which are critical for fostering interaction and establishing trust.
- Well-crafted websites use techniques to maximise conversion rates, directing users towards desired actions like buying something, registering, or getting in touch with the company.
- A website's search engine rankings are influenced by web design components including mobile friendliness, site structure, and page speed, which in turn affects the website's online visibility and discoverability.
- In order to accommodate the wide range of tastes and behaviours of contemporary consumers, responsive web design makes sure that websites adjust fluidly to different devices and screen sizes.
- Unique and user-friendly web design helps a website stand out from rivals in a crowded online marketplace, drawing and keeping consumers in an increasingly cutthroat environment.
Purposeful Design:
- Recognising the aims and objectives of the website and designing with a purpose.
- Adjusting design choices to better suit the target audience's requirements, tastes, and habits.
- Ensuring that the intended message is communicated successfully and that the design directs users towards the required activities.
- Laying out the user journey and creating each stage, from first interaction to conversion, with the main goal in mind.
- Establishing benchmarks and measurements to monitor how well the design fulfils its objectives.
- Giving the target audience's needs, preferences, and behaviours top priority throughout the design process.
- Completing in-depth study to comprehend the target users' motives, characteristics, and problems.
- To represent various target audience segments and guide design decisions, user personas are created.
- Putting the design through iterative testing with actual users to find usability problems and get input for enhancements.
- Embracing a continuous improvement mentality to gradually improve the user experience based on data analysis and user feedback.
- Creating websites with the goal of offering the best possible viewing and interacting experience on a variety of devices, such as tablets, smartphones, laptops, and desktop computers.
- Making use of fluid design ideas and adaptable grid layouts to guarantee that information adjusts to various screen sizes and resolutions without any problems.
- Putting CSS media queries into practice to apply styles according to the device's specs, like screen size, orientation, and pixel density.
- Putting the mobile experience first by creating content for smaller displays and gradually improving the features and layout for larger ones.
- Making sure that content is readable, navigable, and engaging across all devices—regardless of screen size or input method—will improve usability and accessibility.
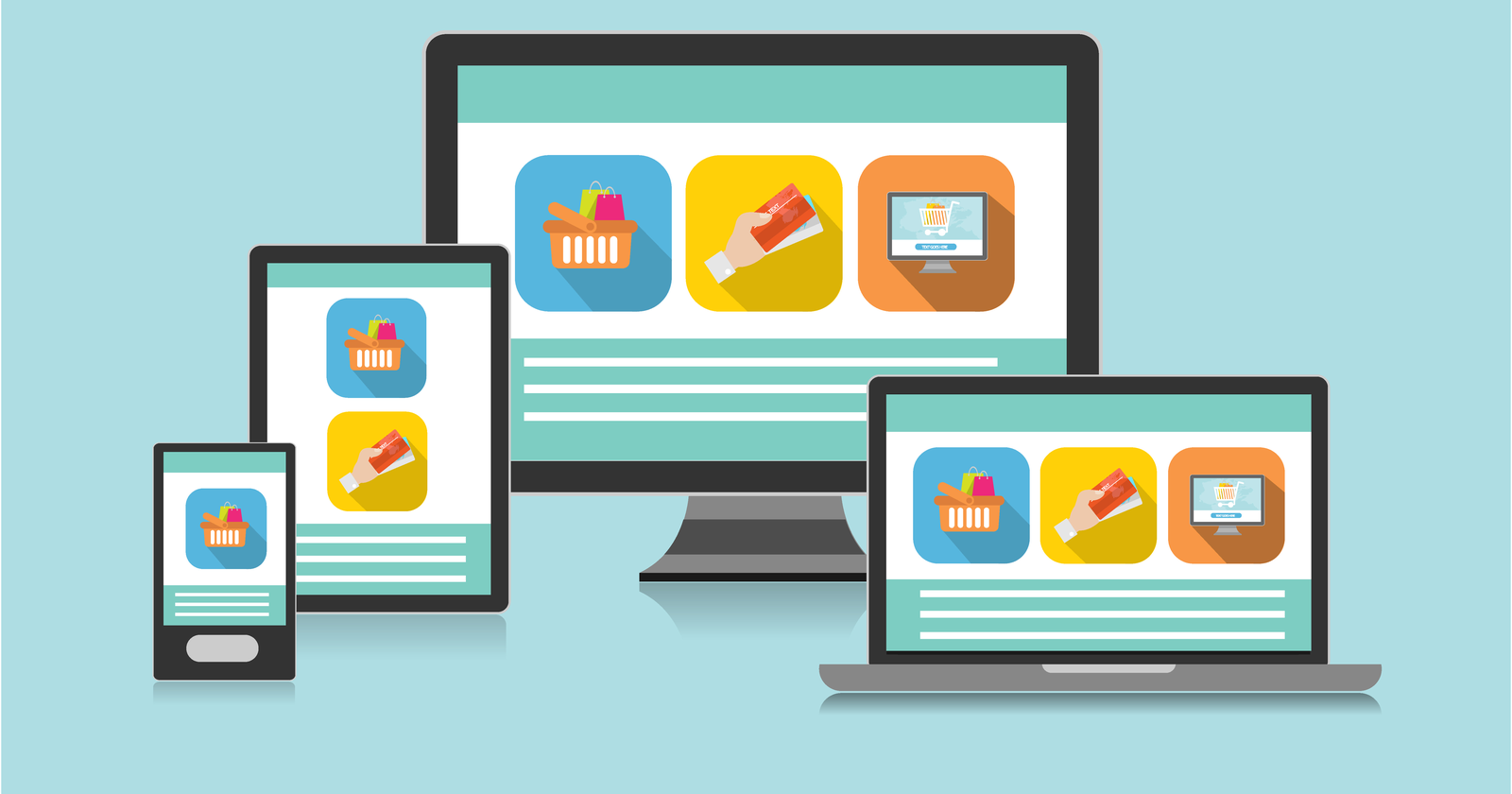

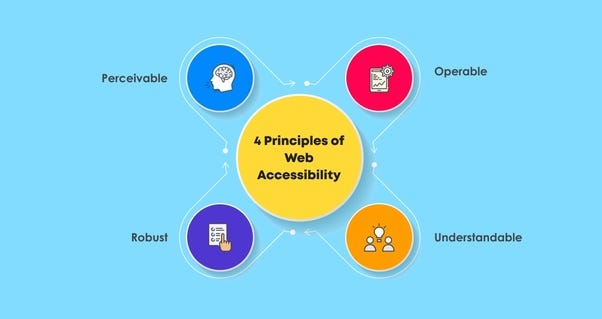
- Ensuring that users with disabilities, such as those with visual, auditory, motor, or cognitive limitations, can use websites.
- Maintaining a universally accessible experience by following accessibility standards and criteria, such as the Web Content Accessibility criteria (WCAG).
- To support users who use assistive technologies, include transcripts for audio and video content, alternate text for images, and descriptive labels for form fields.
- Ensuring that no mouse or other pointing device is needed to access or operate any functionality—all of it can be done using a keyboard alone.
- Ensuring that material is easily understood by individuals with visual impairments or colour vision deficiencies by using appropriate colour contrast and readable fonts.
- Arranging content on a webpage so that it is prioritised for the user based on relevance and importance.
- Making use of contrast in font, colour, and size to highlight vital information, calls to action, and headlines.
- Choosing suitable font sizes, line spacing, and line lengths, as well as avoiding excessively decorative or distracting fonts, will help ensure that content is easy to read.
- Clear visual relationships are created and the user's eye is guided through the page by grouping related things together and aligning them in a visually harmonious manner.
- Creating visual anchors or focus points, such as hero photos, attention-grabbing headlines, or interactive components, that draw users in and point them to the most crucial areas of the page.

- Keeping logos, colours, font, and imagery consistent across the website will help to strengthen brand identification and recognition.
- ensuring that all pages have uniform navigation menus and structures to give users a comfortable and easy browsing experience.
- Applying design components like buttons, forms, icons, and layout patterns consistently will help to strengthen usability and develop a unified visual language.
- preserving a constant tone, voice, and messaging throughout all material in order to create a cohesive brand identity and interact with users in an efficient manner.
- Encouraging user trust and confidence in the website by providing a consistent experience across platforms, devices, and interactions.

- Making an effort to deliver stuff in a clear and succinct manner so that users can quickly understand and absorb it.
- Embracing visual design simplicity by getting rid of extraneous components, clearing off clutter, and concentrating on the most important functions and information.
- Lowering cognitive load, removing distractions, and cutting down on processes to simplify the user journey and produce a seamless, intuitive experience.
- Creating user-friendly menus and navigation systems that lead visitors through the website with ease and help them locate content quickly and effectively.
- To efficiently prioritise content and focus the user's attention, a clear visual hierarchy with noticeable focal points, sensible grouping, and consistent styling should be established.

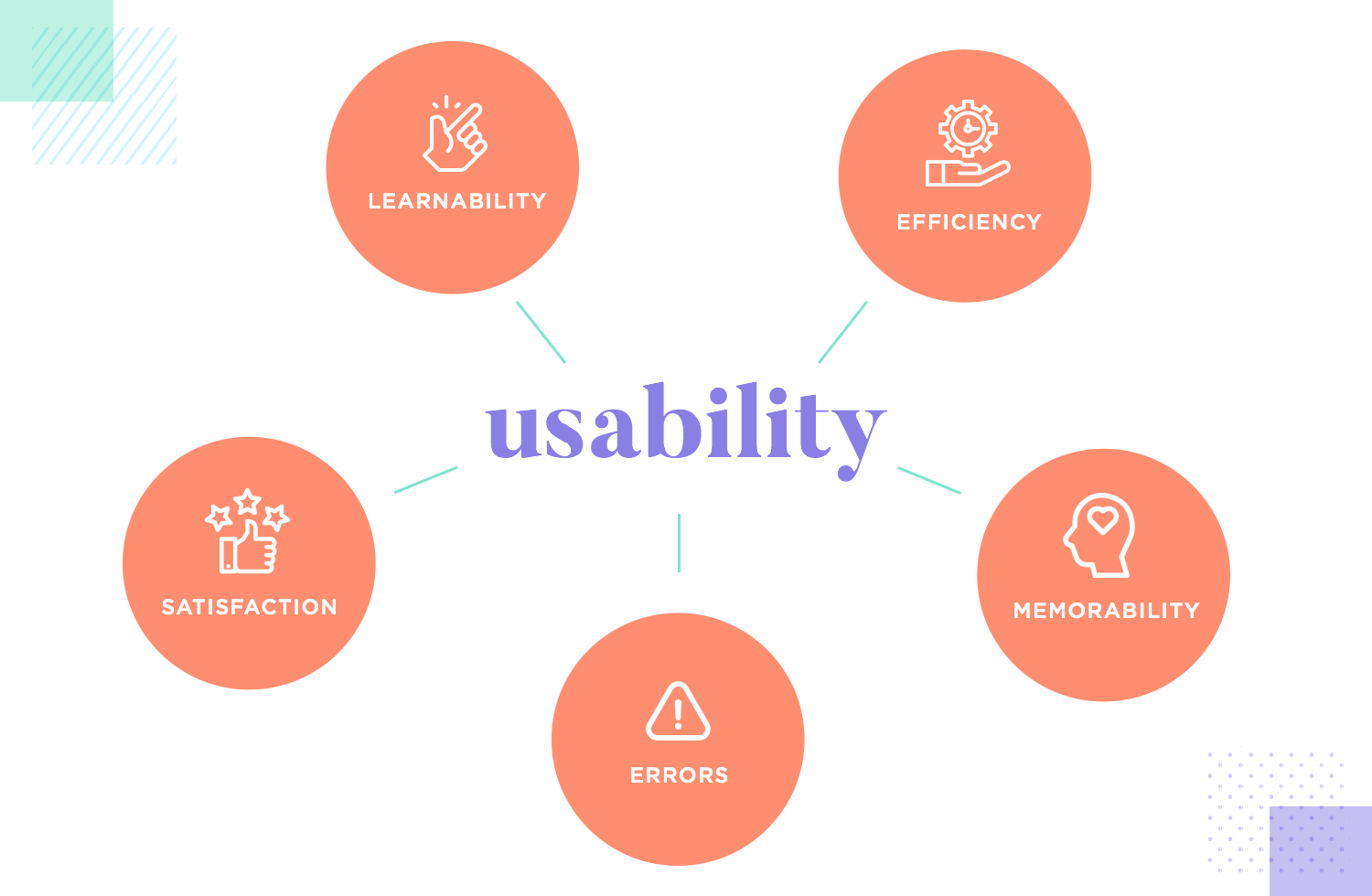
Usability:
- Creating user-friendly navigation menus and structures that make it simple for visitors to locate the information they require and move between the website's many areas.
- Using a standardised page layout and design principles to improve usability, lessen cognitive burden, and give consumers a comfortable and predictable browsing experience.
- Giving users concise feedback messages and error-handling tools will help them finish activities successfully and bounce back from mistakes with grace.
- Real users are used in usability testing to find usability problems, get input, and confirm design choices, making sure the website satisfies user expectations.
Comments
Post a Comment